How Much Insulation Do You Need?
Last time, we talked about conduction (flow of heat within a material or from one material to another). Fiberglass batt and spray foam polyurethane insulation are effective insulators because they are poor conductors of heat – they have a high thermal resistance. The thicker an insulation layer is, the higher R-value it will have.
Convective heat loss (flow of heat through liquids and gases) is reduced by insulation that adequately fills cavities in walls, ceilings, and floors to prevent airflow and drafts. Spray foam polyurethane insulation is ideal because it expands to create a continuous, air-tight wrap of insulation.
Take note: if loose-fill insulation is installed in thick layers, the insulation can compress under its own weight, which reduces the thermal resistance of the insulation and makes it more conductive to heat flow. Similarly, if fiberglass batt insulation is compressed during or after installation for any reason, it’s thermal resistance will decrease.
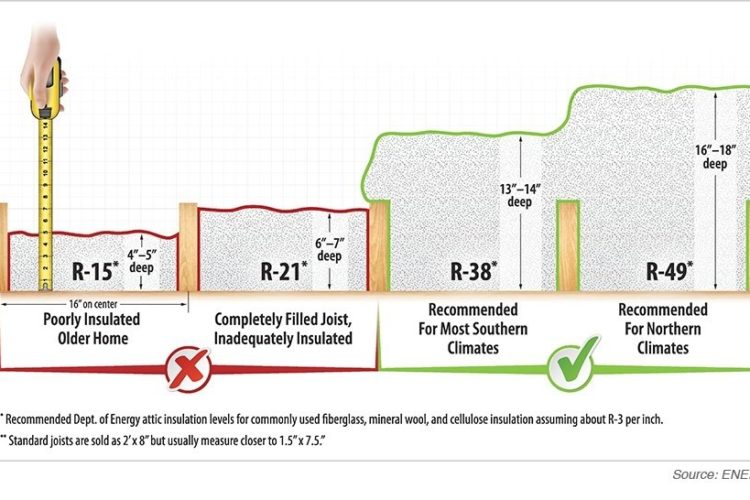
Compare your attic insulation to the image above. Do you need more attic insulation and air sealing in your house? Call Urban Insulation for a free estimate!
Sources: Insulation Institute